Understanding hydrogen-rich compounds under extreme pressure is central to modeling planetary interiors and developing quantum materials. Hydrogen-filled ices, in which hydrogen molecules are trapped within a dense water framework, provide a unique environment where nuclear quantum effects influence both the guest molecules and the host lattice. In this work, researchers employed a quantum embedding model alongside synchrotron X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy to identify the structural signatures of the C2 phase.
The study reveals a “dual quantum locking” effect: hydrogen-bond symmetrization in the water lattice and the orientational ordering of hydrogen molecules proceed in lockstep. This collective alignment, leading to a nematic phase, occurs at remarkably low pressures compared to pure hydrogen due to strong host-guest interactions. These findings refine the high-pressure phase diagram of hydrates and highlight their role as model systems for studying quantum phenomena under extreme confinement.
This work was recently published in PNAS.
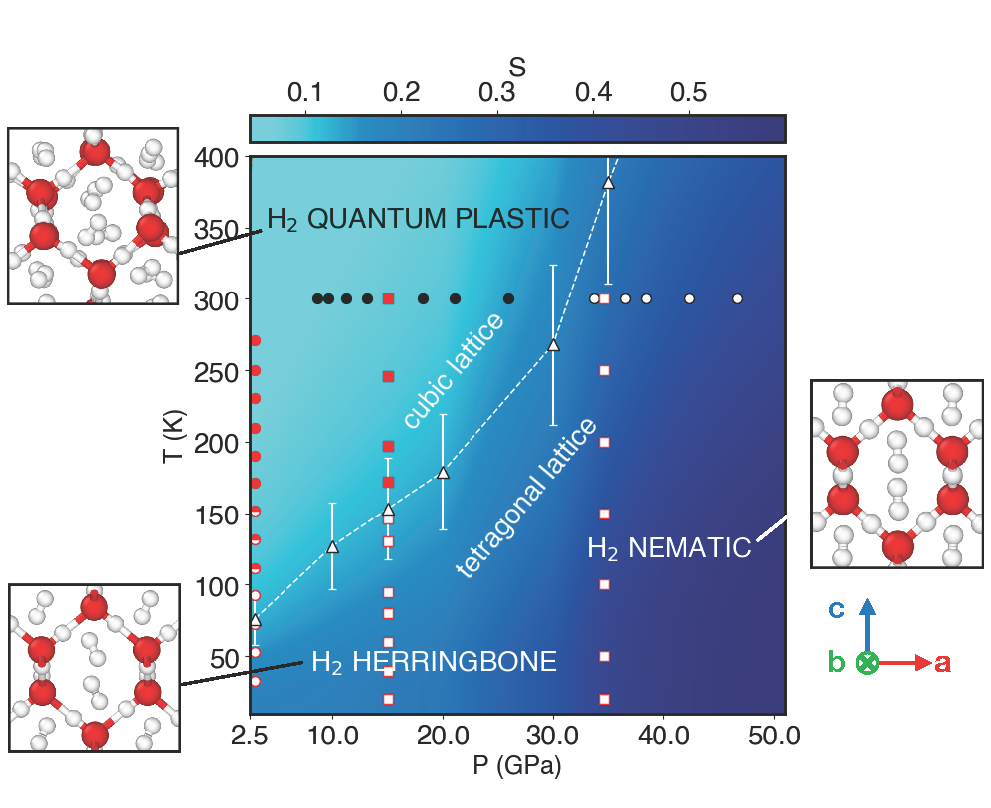
Phase diagram of C2 hydrogen hydrate: Mapping molecular order under pressure.
This figure maps the different orientational states of hydrogen molecules trapped within the ice lattice across various pressure and temperature conditions. The background colors track the transition of hydrogen from freely rotating molecules to highly ordered states. Experimental data are overlaid as circles and squares.
A central finding of our study is that the ordering of hydrogen molecules is directly linked to a structural deformation of the ice: as the molecules align (forming the “nematic” or “herringbone”), the lattice shifts from a cubic symmetry (filled symbols) to a tetragonal symmetry (open symbols).
More:
https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2526369123
Author affiliation:
Laboratoire de physique de L’École normale supérieure (LPENS, ENS Paris/CNRS/Sorbonne Université/Université de Paris)
Corresponding author: Marco Saitta
Communication contact: L’équipe de communication